Erectile Dysfunction
Implantica’s Solution, PotencyFlow®
Implantica’s PotencyFlow® is subject to further development and approval process.
Although Viagra type of drugs has improved the situation for the around 150 million men suffering from Erectile Dysfunction, only 50% are able to use these drugs with a successful result.1
PotencyFlow® is designed to treat impotence by hindering blood leakage from the penis during erection.

The most common cause for erectile dysfunction is leakage of blood from the erectile system since pressurized blood causes the erection. Implantica’s PotencyFlow® is designed to help these patients suffering from erectile dysfunction, which occurs when the blood drains too quickly through the veins. The device, which will use Implantica’s shared wireless energy platform, will be controlled wirelessly by a remote control or a push button under the skin resulting in a smooth chain of events that is expected to lead to a more natural erect penis.
The device is designed to create erection by stimulation followed by restricting the blood flow leaving the penis using a penile blood flow restriction cuff, preventing the leak of the filling blood in the penis, thereby treating erectile dysfunction.
The options available today are reconstructive surgery (often with poor long-term result) or a penile implant. Unlike penile implants, PotencyFlow® will not damage the penile erectile tissue and will therefore be preferred entry procedure especially for patients with some functionality left, having vascular problems.
PotencyFlow® is intended to be controlled wirelessly or by a push button under the skin resulting in a smooth chain of events that is expected to lead to a more natural erect penis.
Surgical procedures to stop the vascular leak have been tried with good results, however, only in the short-term. After a year or two the venous blood system creates new paths expanding small vessels and the symptoms reoccur. However, with an intermittent and short-term closure, such as PotencyFlow®, one could expect this effect to be close to non-existent.
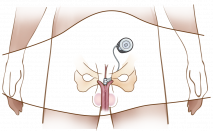
Preventing the leak of the filling blood in the penis will create the possibility for these patients to achieve, and after being stimulated to get erection, keep the erection. Implantica’s solution is expected to be able to help a much larger group of patients than those performing penile implants, due to its additive character.
- 1Frost & Sullivan, 2005
Benefits of PotencyFlow®
Wireless control
Wireless control is designed to enable activation of erection in a controlled and discrete way.
Penis is undamaged
PotencyFlow® is expected to temporarily restrict the blood flow and leave the corpus cavernosum undamaged – unlike current penile implants.
Low complication rate anticipated
Because PotencyFlow® method of treatment is designed to only be active during a short period of time, the risk of complications is likely reduced.
Field Description
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) can be defined as ‘the inability to achieve an erection satisfactory for sexual intercourse. Satisfaction is determined by both patient and partner, making ED a ‘couple’s disease’. The degree of ED can range from a total inability to achieve an erection, an inconsistent ability to do so, or a tendency to sustain only brief erections. The World Health Organization specifies a three-month minimum duration of symptoms to establish the diagnosis. Approximately 5% of 40-year-old men and 15-25% of 65-year old men suffer from complete ED.2
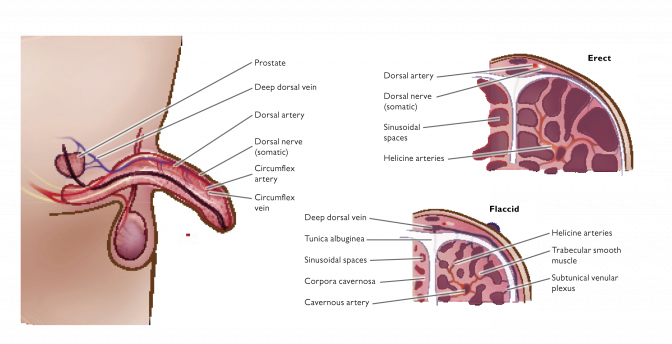
The penis has two chambers called the corpora cavernosa, which run the length of the organ and are filled with spongy tissue. The corpora cavernosa are surrounded by a membrane called the tunica albuginea. The spongy tissue contains smooth muscles, fibrous tissues, spaces, veins and arteries. The urethra runs along the underside of the corpora cavernosa in the corpus spongiosum and is the channel for urine and ejaculate.
An erection is a complex, involuntary, neuropsychological, hormone-mediated, vascular event, which begins with both sensory and mental stimulation. Impulses from the brain and local nerves cause the muscles of the corpora cavernosa to relax, which allows rapid blood flow to fill the spongy chambers, thus creating pressure in the corpora cavernosa and expanding the penis. An erection is sustained when the tunica albuginea helps trap the blood within corpora cavernosa, but is reversed when the muscles in the penis contract, which stops the inflow of blood and opens the outflow channels.
- 2Brooks & Jordan, 2001; nKUIDC, 2007
Existing Treatments
Usually, oral drugs are the first step in ED treatment and are referred to as first line treatment. However, these drugs only treat 50% of a group of 150 million men. Penile injection has been used as a second line treatment for over a decade. It has a higher success rate than drug treatment, but it is not generally considered a popular form of treatment with patients because of the need to administer regular self- injection into the corpora cavernosa of the penis.3
Urethral suppositories are another alternative. Following urination, a small pellet is inserted approximately an inch deep into the urethra via an applicator at the tip of the penis. The pellet contains alprostadil. The method is just slightly easier to self-administer than injections and it also suffers from the lack of spontaneity.
Patients generally have tried both drugs and other treatments before they are considered suitable for third line treatment. The use of drugs like Viagra and new competitors producing implants have caused a rapid increase in the use of penile implants. In some cases, surgery is used to repair damaged arteries and tie off veins. The most common method is penile venous reconstructive surgery, also called venous ligation. This is a method used when the blood drains out too quickly through the veins. If this occurs, the veins that drain the penis may be tied off, however, because new veins develop over 1-2 years time and again cause leakage of blood from the erected penis, this method has not been very successful in the long run.
Penile prostheses for the treatment of ED have been available for more than 30 years in the US. A key discovery in the field of penile prosthetics was that the corpora cavernosa could be accessed surgically without damaging the penile vessels, urethra or sensory nerves. Intracorporal cylinders can then be installed.4
The most commonly used implants are multi-component inflatable implants, consisting of two or three components. Inflatable cylinders placed in the corpora cavernosa, a fluid reservoir implanted in the abdomen or lower pelvis and a small pump placed in the scrotum. The user squeezes the pump and fluid moves from the reservoir into the cylinders to create an erection. A further squeeze of the pump reverses the process.
The main problem with penile implants is that the normal functionality is damaged permanently, meanwhile a devise like PotencyFlow® adds to your exiting functionality.
- 3Belsley et al., 1998; Brooks & Jordan, 2001
- 4Garber, 2005
Detailed Treatment Field Information
Implantica is developing products for the treatment of Erectile Dysfunction (ED). The company is focused on high technology products which are designed to help patients attain a higher quality of life and provide benefits over current existing products by being easier to use and generally more acceptable to the patient population.
Overview
Formerly known as ‘impotence’, the term Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is now more often used to distinguish it from other problems related with sexual intercourse, e.g. lack of sexual desire or ejaculation and orgasm problems (Brooks & Jordan, 2001). ED is treatable and not a life-threatening disease. However, the condition may result in numerous social and personal problems: depression, withdrawal from sexual intimacy, marital problems, reduced quality of life, decreased working productivity, and increased healthcare utilization (Dhanani et al., 1998, cited by Joyce et al., 2007). With the introduction of Viagra in 1994, the market for erectile dysfunction treatments boomed. Still, many men hesitate to seek help due to the social stigma and embarrassment associated with ED.
Description and definition
Erectile Dysfunction was defined at the National Institutes of Health Consensus Conference in Washington DC, US, December 1992 as ‘the inability to achieve an erection satisfactory for sexual intercourse’ (National Institutes of Health, 1993). Satisfaction is determined by both patient and partner, making ED a ‘couple’s disease’. The degree of ED can range from a total inability to achieve an erection, an inconsistent ability to do so, or a tendency to sustain only brief erections. The World Health Organisation specifies a three-month minimum duration of symptoms to establish the diagnosis (WHO cited by Joyce et al., 2007).
Approximately 5 % of 40 year old men and 15-25 % of 65 year old men suffer from complete ED (Brooks & Jordan, 2001; NKUIDC, 2007).
The penis has two chambers called the corpora cavernosa, which run the length of the organ and are filled with spongy tissue. The corpora cavernosa are surrounded by a membrane called the tunica albuginea. The spongy tissue contains smooth muscles, fibrous tissues, spaces, veins and arteries. The urethra runs along the underside of the corpora cavernosa in the corpus spongiosum and is the channel for urine and ejaculate.
An erection is a complex, involuntary, neuropsychological, hormone-mediated, vascular event, which begins with both sensory and mental stimulation. Impulses from the brain and local nerves cause the muscles of the corpora cavernosa to relax, which allows rapid blood flow to fill the spongy chambers, thus creating pressure in the corpora cavernosa and expanding the penis. An erection is sustained when the tunica albuginea helps trap the blood within corpora cavernosa, but is reversed when the muscles in the penis contract, which stops the inflow of blood and opens the outflow channels.

Causes and effects
As previously mentioned, there is a well-defined sequence of events that take place to enable an erection. ED can occur when any of these events are disrupted. Brooks & Jordan (2001) states the cause in more than 75 % of the cases is physical rather than psychological and that the most common cause is damage either to arteries, smooth muscles or fibrous tissues and those damages accounts for approximately 70 % of the cases.
The condition can be categorized as psychological or physical or both. Psychological factors include stress, anxiety, and guilt, lack of self-esteem, depression, and fear of sexual failure. Physical factors are more prominent, and can be things such as:
System diseases, for example: cardiac, hepatic, renal, pulmonary, cancer, metabolic, post organ transplant, pelvic irradiation.
Androgen deficiency, as androgen resistance, other endocrinopathies.
Vascular insufficiency, like atherosclerosis, pelvic steal, penile Raynaud’s syndromE, venous leakage.
Neurological disorder: Parkinson’s, Alzheimer’s, Shy-Drager, encephalopathy, spinal cord or nerve injury.
Penile disease: Peyronie’s disease, priapism, phimosis, smooth muscle dysfunction, trauma.
Many of the above causes of this disease relate to high age. Joyce et al. (2007) states that 69.4 % of all 70-76 year old men suffer from erectile dysfunction to some extent. In this study, at the age of 50-54, 26.0 % of all men have ED, which supports the above statement.
In the US, erectile dysfunction is more common among obese men and men with diabetes (Carson et al., 2007).
ED is and will continue to be a significant problem. Today patients developing ED generally have a higher expectation in terms of quality of life and the effects of ED will most certainly be even harder to cope with for these patients.
Existing treatments
Due to the many different causes of ED there are numerous treatment methods, spanning from oral drug treatment to surgical methods such as penile implant. However, most physicians agree that the treatment path adopted should begin with the least invasive and end with the most invasive procedure. The steps are usually referred to as first, second and third line treatment. The primary goal of treatment is to restore satisfactory erections with minimal adverse effects.
In case of psychological causes, the urologist refers the patient to a qualified psychologist, psychiatrist, sex therapist or marriage counsellor. This treatment line is not included here, as Implantica’s device is not designed for the use such patients.
First line treatments
Usually, oral drugs are the first step in ED treatment and are referred to as first line treatment. There are a number of pharmaceuticals used to treat erectile dysfunction, the most common being so called PDE5 inhibitors.
- Oral drugs
Oral drug treatment is relatively easy to explain and maintain and patients are easy to motivate. Many different agents exist, but in recent years, two groups of agents have become the most commonly used:
Phosphodiesterase (PDE5) inhibitators. The erection process involves the release of nitric oxide (NO) in the corpus cavernosum. This step increases the levels of cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP), which leads to smooth muscle relaxation (vasodilation) in the corpus cavernosum, which in turn increases in the inflow of blood. The most known phosphodiesterase-5 (PDE5) inhibitor Sildenafil Citrate (Viagra™) was introduced in the US in 1998. It is one of three oral PDE5 treatments used today (the other two being Cialis™ and Levitra™). These inhibitors act as erection enhancers, i.e. the patient’s normal sex drive is not affected directly but the ability to get a full erection is enhanced. They are not suitable for patients that take nitrates for angina or hypertension. Common side effects include headache, dizziness, facial flushing, sneezing and visual changes (due to its effect on PDE6, which is present in the retina of the eye) (Pfizer, 2007). About 30 % of men fail to respond to PDE5 inhibitors and another 20 % suffer significant side effects (McCullough, 2007).
Dopamine agonists. Apomorphine is a dopamine receptor agonist that stimulates dopamine D1 and D2 in the brain to induce erection by producing signals to begin the erectile process. This drug can be taken orally, but is more effective in its sublingual (under the tongue) and intranasal (through the nose) administration forms.
There are other oral agents developed for ED treatment, for example different types of oral testosterones, but they are not commonly used. The reason is that PDE5 inhibitors such as Viagra are efficient and currently dominate the market (Frost & Sullivan, 2005).
Second line treatments
- Penile injections
Penile injection has been used as a second line treatment for over a decade. It has a 70-90% success rate, higher than PDE5 inhibitors, but it is not generally considered a popular form of treatment with patients because of the need to administer regular self-injection into the corpora cavernosa of the penis (Belsley et al., 1998; Brooks & Jordan, 2001). The most common drug is prostaglandin E1 under the name Alprostadil. This drug is a vasodilator, which causes blood vessels to expand and thus blood flow to the penis increases. The use of injections can lead to scarred tissue and risk of wrong dosage that in severe cases damaged tissue in the corpora cavernosa.
Alprostadil usually begins to work in about 5 to 20 minutes. Intercourse should be attempted within 10 to 30 minutes after using the medication. This will produce an erection that lasts about an hour. An erection may continue after ejaculation. It is advised to use no more than three times per week with at least 24 hours between each use.
There is a reported 37-70 % dropout rate, mostly due to fear of injections or lack of spontaneity (Kandeel et al., 2001; British Society for Sexual Medicine, 2007). With a better method of treatment the high dropout rates will certainly fall. Furthermore, an easier method of drug delivery may reach a broader patient group, patients that cannot take injections due to various problems.
- Urethral suppositories
This is another second line treatment, but without the injections. Following urination, a small pellet is inserted approximately an inch deep into the urethra via an applicator at the tip of the penis. The pellet contains Alprostadil. It is most commonly known under the name of MUSE, “medicated urethral system for erection”. Since the introduction of above mentioned oral PDE5 inhibitors, urethral suppositories have diminished. The method is just slightly easier to self-administer than injections and it also suffers from the lack of spontaneity.
- Other drug delivering methods
Due to the scaring of injections of Alprostadil and the cardiac side effects of existing oral treatments such as Viagra, intranasal therapy and topical therapy are interesting alternatives for future patients.
Intranasal therapy method uses a faster way of delivering an active substance for ED patients through the nose. Using this method gives rapid drug absorption via highly vascularised mucosa and a rapid onset of action (Frost & Sullivan, 2005).
Topical therapy is a method already existing under the name of Befar (with Alprostadil) produced by NexMed. It is a cream that delivers the active substance through the skin. It is applied to the opening of urethra and is therefore a less invasive way than injections.
- Vacuum pump
Mechanical vacuum devices cause an erection by creating a partial vacuum around the penis, which allows the inflow of blood and the penis to engorge and expand in a way similar to a natural erection. The device is made of three necessary components: a plastic cylinder that covers the penis, a hand or battery pump, which draws air out of the cylinder, and an elastic ring, which is fitted over the base of the penis and maintains the erection. A typical erection lasts up to 30 minutes using a vacuum pump and should not be longer because of the development of ischemia (absolute or relative shortage of the blood supply to an organ)
Third line treatments
Patients generally have tried both drugs and other treatments before they are considered suitable for third line treatment. Of all ED patients, 6-10 % reaches these invasive treatment methods (HBS Consulting, 2007). Approximately 25 000 patients every year are treated with penile implants/prosthesis (AMS, 2006).
- Surgery
In some cases, surgery is used to repair damaged arteries and tie off veins. The most common methods are called:
Penile venous reconstructive surgery, also called venous ligation, is a method used when the blood drains out too quickly through the veins. If this occurs, the veins that drain the penis may be tied off. This type of dysfunction is often called Corporal Veno-Occlusive Dysfunction (CVOD).
Penile arterial reconstructive surgery, also called penile revascularization, is a method used in younger men who have injuries that affect blood flow to the penis. During surgery, a portion of a blood vessel from elsewhere in the abdomen is used to bypass the damaged portion of artery that supplies blood to the penis.
- Penile implants
Penile prostheses for the treatment of ED have been available for more than 30 years in the US. A key discovery in the field of penile prosthetics was that the corpora cavernosa could be accessed surgically without damaging the penile vessels, urethra or sensory nerves. Intracorporal cylinders can then be installed. (Garber, 2005)
The used implants can be divided into three main categories:
- Semi-rigid rods, which consists of two bendable rods, with the outer surface of each being silicone and the inner component being silver or stainless steel wires or interlocking plastic joints held together with a cable. Once implanted, the penis can be manually bent up or down as required by the user. The rods can be implanted as an outpatient procedure using local anaesthetic. The major disadvantage is that the penis has to be well hidden under clothing since it is permanently stiff, even when bent down.
- Self-contained devices, where two cylinders are placed inside the penis, each one containing a pump, fluid and a release valve. A squeeze to the head of the penis forces fluid to transfer and cause rigidity. Conversely, bending the penis forces the fluid back to the storage area.
- Multi-component inflatable implants, consisting of two or three components. Inflatable cylinders placed in the corpora cavernosa, a fluid reservoir implanted in the abdomen or lower pelvis and a small pump placed in the scrotum. The user squeezes the pump and fluid moves from the reservoir into the cylinders to create an erection. A further squeeze of the pump reverses the process.
Numerous studies show that penile implants have a very high satisfaction rate. According to European Association of Urology (EAU), the overall satisfaction rate is as high as 70-87 %. The dominating implant is the multi-component with three components (see Figure 4), which accounts for 75 % of all implants (HBS 2007). The most commonly mentioned problems with the inflatable 3-piece implants are unwanted erections due to mechanical pump functionality, unnatural appearance of scrotum (pump is placed there), and the lack of spontaneity due to the manual pump.
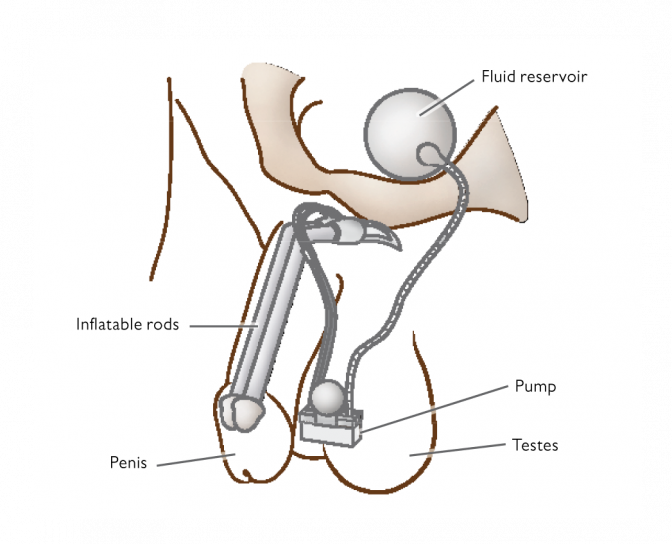
Fig. 4
Socio-economic burden
It is difficult to estimate the costs for society that are related to erectile dysfunction. However, there are some studies in the area that make an effort to quantify that very cost.
A prevalence-based cost of illness study was performed from the perspective of the UK National Health Service (NHS), to evaluate the annual direct cost of managing Erectile Dysfunction (ED) between 1997 and 2000. The main outcome and result for 2000 was that the total direct cost for the UK society (in this case NHS) of managing ED was estimated at USD 110 million (GBP 74 million) (Brown et al., 2002). By extrapolating the UK cost to the European and the US population, we estimate the total direct cost for society of managing ED in these geographic areas at USD 2 billion. Quality of life and affect on mental health parameters should not be underestimated.