Europe
RefluxStop™ is CE marked in Europe. It is currently available in:
- Germany
- United Kingdom
- Switzerland
- Spain
- Italy
- France
- Austria
- Sweden
- Norway
Follow-on Products
Gastrointestinal
Implantica’s StomaRestore® is subject to further development and approval process and is not yet on the market.
StomaRestore® is designed to free patients who need an ostomy operation or existing ostomates from using stoma bags, which could greatly improve their quality of life. Many patients need to remove part of their intestine due to illness and therefore receive a stoma, which is when the end of the intestine protrudes through the abdominal wall. These patients use a plastic bag to collect their fecal matter outside the abdominal wall. StomaRestore® is designed to offer a completely new solution to those patients and could potentially free patients from using stoma bags.
StomaRestore® could potentially free patients with a stomy from using stoma bags.
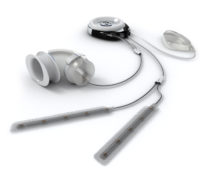
StomaRestore® is designed to be controlled wirelessly with an artificial sphincter using electrical stimulation in such a way that is expected to mimic the bowel organs’ natural function.
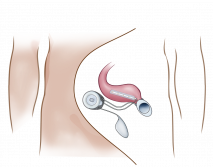
StomaRestore® is designed to offer a sphincter function and to control the emptying of a reservoir made from the intestines. The reservoir should prolong the time in between bowel emptying. A muscle contraction of the intestinal wall causes emptying of the reservoir at patient’s will. StomaRestore® is designed to use a combination of hydraulic pressure and electrical stimulation to help control the flow of liquids and food passing through the intestine.
As Mentioned, Implantica’s StomaRestore® is subject to further development and approval process and is not yet on the market. It is designed to:
Thus, StomaRestore® is designed to avoid plastic stoma bags outside the abdominal wall for the collection of fecal matter, intended to significantly increase patients’ quality of life and may provide them with a permanent freedom from the constraints of having to wear and regularly change the plastic bag.
The closing pressure of StomaRestore® is designed to vary in position, which should allow for optimal blood circulation and permit time for recovery.
A reservoir will be created using the intestine itself. The device is designed to empty the reservoir using natural muscle wall contractions applying electrical stimulation.
Ostomy surgery is a treatment method for severe intestinal disease in the abdomen. It is also the end alternative when all other treatment methods fail for fecal incontinence. An ostomy is a surgically created opening of the intestines and the abdominal wall through which waste material passes out of the body from the bowel. A stoma is the end of the bowel, protruding through the abdominal wall. After ostomy surgery, patients need to wear a stoma bag for collection of bodily waste often for the rest of their lives.
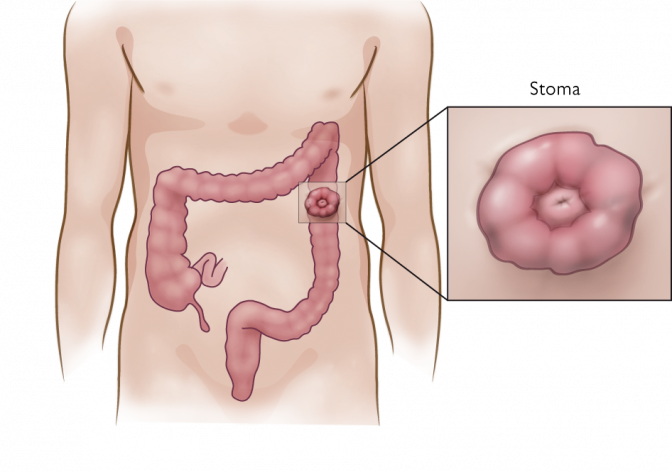
Different types of ostomy procedures are performed depending on how much and what part of the intestine is removed. Colostomy refers to a surgical procedure where a portion of the large intestine is brought through the abdominal wall to carry stool out of the body, meanwhile an ileostomy refers to the small intestine, brought through the abdominal wall and in this case collecting floating fecal matter. In both cases patients must wear a plastic stoma bag over the stoma to collect all waste. Sometimes the intestine can be operated back into the abdomen, however, often it’s a permanent solution.
The end of the ileum, which is the lowest part of the small intestine, is brought through the abdominal wall to form a stoma due to illness or lack of the large intestine called colon. A plastic stoma bag is usually attached to the abdominal wall to collect waste matter, which is liquid when it reaches the ileum. An ileostomy may be temporary or permanent and when permanent often involve removal of a part of or the complete colon.
The causes for needing ostomy surgery include chronic disease in the intestine such as inflammatory bowel disease (mainly Morbus Crohn and Ulcerous colitis), intra-abdominal infection, injury to the colon or rectum, colon/rectal cancer or wounds or fistulas.
People of all ages are affected and whether the ostomy is temporary or permanent depends on the specific disease or injury. Ostomy surgery severely impacts quality of life and can significantly affect the patient’s self-image. Additional problems associated with ostomy include leakage from the stoma, allergic reaction and food blockages, leakage of mucous and bleeding from anus or prolapse.
An ostomy involves creating a stoma, an artificial opening on the abdominal wall, through which waste material passes out of the body from the bowel (or urinary tract). Patients need to wear a stoma bag for collection of bodily waste, often for the rest of their lives.
The terms ostomy and stoma are often used interchangeably, although they have different meanings: An ostomy refers to the surgical procedure to create an opening in the body, while a stoma is the end of the bowel, protruding through the abdominal wall.

Fig. 4
Ileostomy is the mot common permanent ostomy surgery
Ileostomy is a surgical procedure in which the lowest part of the small intestine (ileum) is attached to the abdominal wall. Digestive waste then exits the body through a stoma located on the abdominal wall. A stoma appliance is normally attached to the abdominal wall to collect fecal matter.
An ileostomy may be temporary or permanent, and involves removal of a part, or all, of the colon. Because fecal matter from the small intestine is liquid, it is difficult to maintain continence. Per day 2-3 liters of fluid passes through an ilestomy since the liquid is normally absorbed in the colon, the lower part of the intestine. Since the late 1970s, different types of surgery creating reservoirs have been tested with limited success. All of the methods create problems, such as frequent toilet visits and a high incidence of perianal skin problems. In addition, to be a candidate for this type of surgery, the patient needs an intact anal sphincter, which is rarely the case (American Cancer Society, 2008b).
The socio economic burden of fecal incontinence (FI) and ostomy surgery is substantial. A major problem for patients suffering from FI is the high risk of infection, which prolongs the hospital stay and need for after care. If treated, these patients can enhance their quality of life and become able to return to work. Resources can be released and used within other areas of society.
FI has a dramatic impact on the health care system, as existing treatments are often complicated and associated with high costs. The cost of today’s commercially available artificial sphincters ranges from USD 6 400 to 16 000, since the infection risk to place one surgically is about 50%, these methods have not had any success. This can be can be compared to the long-term cost of treatment of FI secondary to childbirth injury, estimated at more than USD 17 000 per patient (Person & Wexner, 2005).
Items with the strongest impact on the overall cost of FI are: incontinence material (diapers, pants, nappies, anal tampons, waterproof sheets, feces bags etc.), which accounts for a large part of total expenditures. For instance in the US, FI accounts for more than USD 400 million per year for adult diapers only (Kalantar, Howell & Talley, 2002). In addition, it is the second leading cause of admission to long-term facilities in the US (Person & Wexner, 2005).
Furthermore, a large proportion of direct as well as indirect health care costs involved with FI, derive from the cleaning of incontinent patients. It has been estimated that personnel in charge of caring for incontinent patients who are permanently in institutions, devote more than 13% of time available to this duty. However, the cost of health care personnel is not limited only to time and salary. Staff members who spend much of their time cleaning incontinent patients are more prone to dissatisfaction, depression and infection than are those engaged in other activities, and they are more likely to give up their jobs. (Ratto, Ponzi, Di Stasi & Parello, 2007)
Implantica is developing products with the aim to offer more effective treatments, facilitating for surgeons and patients and thereby striving to reduce costs for hospitalization, medication and after care.
Stomy surgery has a considerable impact on a patient’s quality of life. The methods of avoiding a stoma and connecting the small intestine to the anus still have too many problems to be an attractive method for most patients. These methods are sometimes used because no better option is at hand. Implantica is developing a solution for patients who need, or have had, ostomy surgery with products that are designed with the goal to permanently free patients from using ostomy bags. Implantica’s new device is designed to be placed around the intestine to enable the patient to control when to empty the bowel; an alternative to stoma bags, this solution is designed to enable patients to live a normal life with physical exercise and intimacy.